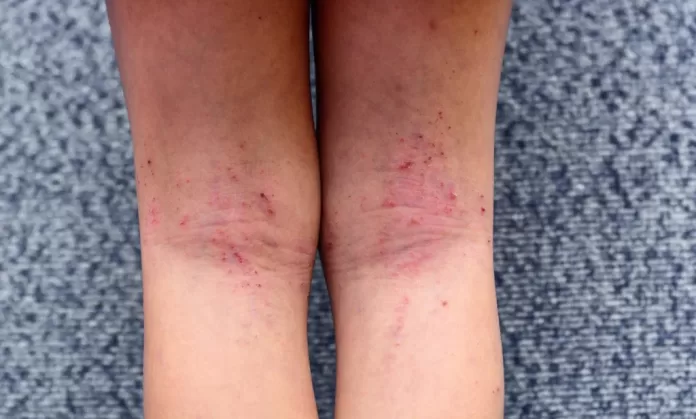
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, characterized by itchy, inflamed, and often painful patches of skin. While this condition typically begins in childhood, it can persist into adulthood or even begin later in life. Understanding atopic dermatitis is crucial for managing its effects and improving the quality of life for those affected.
The Basics of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is one of the most common skin conditions. It is part of the “atopic triad,” which also includes asthma and hay fever. This indicates that many individuals with atopic dermatitis may also experience one or both of the other conditions. The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, but it is believed to be linked to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis vary widely among individuals, with common symptoms including red or brownish-gray skin patches, intense itching, especially at night, dry and scaly skin, and thickened, cracked, or swollen skin. In some instances, tiny bumps may appear, which can leak fluid and crust over if scratched. It is essential for individuals to identify these symptoms early for effective management.
Identifying Triggers
Managing atopic dermatitis effectively begins with identifying and avoiding triggers. Common triggers include stress, allergens like pollen and pet dander, harsh soaps and detergents, and severe temperature changes. Recognizing these triggers can help in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups, enabling individuals to better manage their condition.
Treatment Options Available
A variety of treatment options are available, ranging from over-the-counter moisturizers to prescription medications. Initial treatments often involve moisturizing creams designed to keep the skin hydrated and reduce inflammation. Corticosteroid creams are a common treatment to alleviate inflammation and itchiness. In more severe cases, oral medications like antihistamines and immunosuppressants may be prescribed.
Developing a Consistent Skincare Routine
One of the best defenses against atopic dermatitis is a consistent skincare routine. This includes keeping the skin moisturized, especially after bathing, using gentle cleansers, and avoiding products with harsh chemicals. Moisturizers should be applied multiple times a day to prevent the skin from drying out and to help maintain the skin’s natural barrier function.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Research into atopic dermatitis continues to evolve, with new treatments offering hope for better relief and management. Emerging therapies include biologics, which target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation, and advancements in topical treatments that improve skin barrier function. Staying informed about these developments is essential for those seeking the latest and most effective management strategies.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Management
Adapting certain lifestyle habits can significantly improve the management of atopic dermatitis. Wearing soft, breathable fabrics can reduce irritation, and keeping a clean living environment minimizes exposure to allergens. Additionally, managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga can be beneficial, as stress is a known trigger for flare-ups.
The Importance of Professional Guidance
While self-care and knowledge are crucial, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for tailoring a treatment plan to an individual’s specific needs. Dermatologists or allergists can offer expert advice and might suggest treatments that are not yet widely available. Regular consultations can also provide updates on the latest treatment options and research findings.
Educational Resources
For ongoing support and information, websites like HealthFunda.net provide a wealth of resources that can help individuals stay informed about atopic dermatitis. These platforms offer advice, tips, and the latest research to aid in managing this condition effectively. Engaging with such resources empowers patients with knowledge and practical strategies to improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
Living with atopic dermatitis can be challenging, but understanding the condition, identifying triggers, and seeking appropriate treatment can lead to effective management and improved well-being. By maintaining a strong routine and staying informed about new developments, individuals can significantly reduce the impact of atopic dermatitis on their lives.