Maintaining heart health is crucial for living a long and healthy life. Heart attacks, one of the most prevalent yet preventable health crises, affect millions of people worldwide. Understanding the signs, causes, risk factors, and prevention strategies can significantly improve your chances of avoiding this life-threatening event.
What is a Heart Attack?
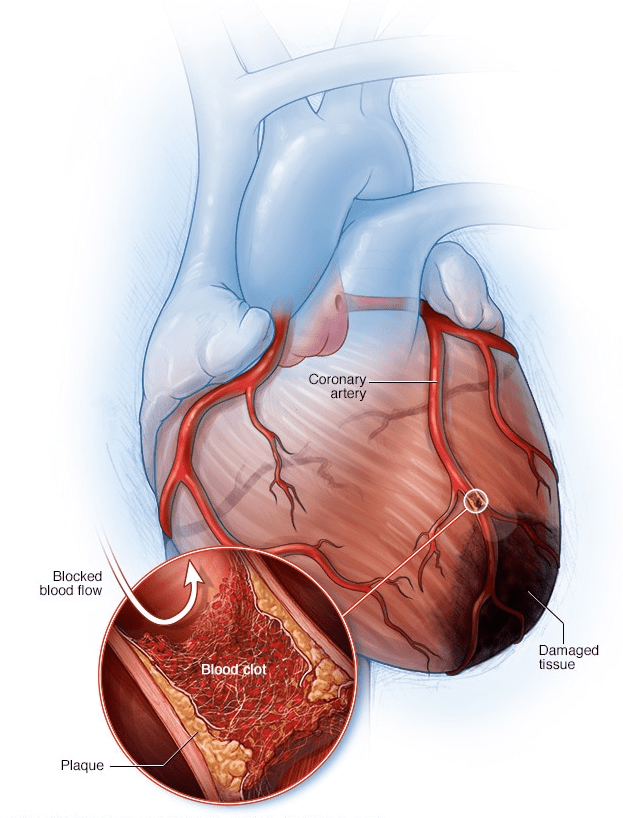
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of the heart muscle is blocked. If the blood flow isn’t restored quickly, the heart muscle begins to die. This can have severe implications for overall health, often leading to long-term complications or even death. Heart attacks are a leading cause of death globally but are largely preventable with the right knowledge and lifestyle choices.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a heart attack is critical for seeking immediate medical attention and increasing the chances of survival. Common signs include:
- Chest Discomfort: Pain, pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation in the center of the chest.
- Upper Body Pain: This can extend to the shoulders, arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Shortness of Breath: Often accompanied by chest discomfort, which can occur even without physical exertion.
- Cold Sweat: Breaking out in a cold sweat without any apparent cause.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling nauseous or vomiting can be signs, especially in women.
- Lightheadedness or Dizziness: Feeling faint or dizzy can indicate a reduced blood flow to the brain.
Atypical Symptoms
Atypical symptoms that are often overlooked, especially by women, include:
- Unusual fatigue
- Indigestion or heartburn
- Pain in the throat or upper abdomen
Causes of Heart Attacks
Understanding what leads to a heart attack can help you adopt preventive measures. Some primary causes include:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the coronary arteries, narrowing them and restricting blood flow.
- Blood Clots: When plaque in a coronary artery ruptures, it can form a blood clot that blocks the artery.
- Spasm of a Coronary Artery: A temporary reduction in blood flow to part of the heart muscle.
Risk Factors
Various factors increase the risk of heart attacks, some of which are controllable while others are not. Key risk factors include:
- Age: Risk increases with age, particularly after 45 for men and 55 for women.
- Family History: A history of heart disease in the family can elevate risk.
- High Blood Pressure: Puts extra strain on the heart and arteries.
- High Cholesterol Levels: Leads to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Diabetes: Increases the risk due to associated high blood sugar levels.
- Obesity and Physical Inactivity: Contributes to other risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and unhealthy cholesterol levels.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: Damages blood vessels and heart tissue.
- Poor Diet: High in fats, sugars, and salt can lead to heart disease.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing heart attacks involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and making informed choices. Here are practical tips:
- Healthy Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Quit Smoking: Seek resources to help quit smoking, as it greatly reduces heart attack risk.
- Limit Alcohol Use**: Moderate alcohol consumption or avoid it altogether.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regularly monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes.
Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection of heart disease can save lives. Regular health check-ups are paramount for identifying risk factors. If you suspect you’re having a heart attack, seek immediate medical care. Treatment typically involves medications, lifestyle changes, and possibly surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
Recovery and Lifestyle After a Heart Attack
Recovery from a heart attack involves both physical and emotional adjustments. Here are steps to ensure a smoother recovery:
- Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs: Participate in structured programs to improve heart health.
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere to prescribed medication and follow-up appointments.
- Adopt a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle: Continue with healthy eating, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Support System: Lean on friends, family, or support groups for emotional support.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Heart attacks are serious but largely preventable with the right knowledge and actions. By understanding the signs and symptoms, addressing risk factors, and adopting preventive strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk.
For personalized advice and support, book a consultation with one of our heart health specialists today. Prioritize your heart health—your life depends on it.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure a healthy heart and a longer, more fulfilling life. Stay proactive and informed about your heart health, and take the necessary steps to protect yourself and your loved ones.
For more insightful articles and health tips, visit our Health category. Discover insightful health tips today and empower your well-being!


