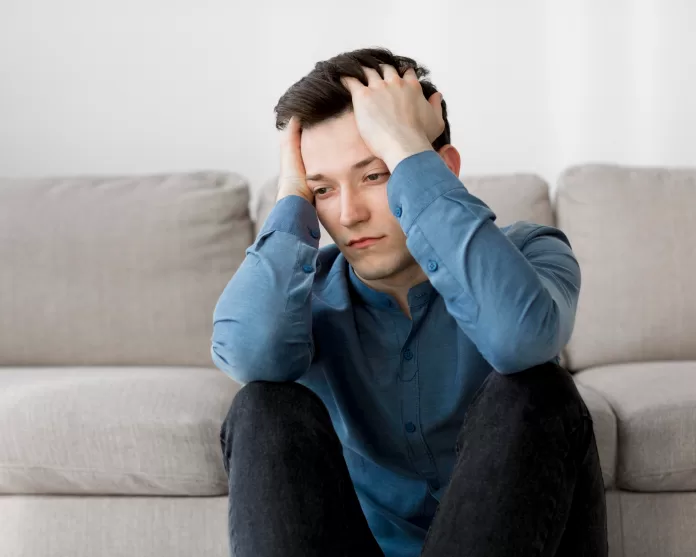
Depression is often perceived primarily as a mental health condition, yet it manifests in a myriad of physical symptoms that can be just as debilitating. These symptoms not only affect one’s mood but also have profound impacts on physical well-being, often compounding the challenges faced by those living with depression. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore these physical manifestations, their impact on daily life, and offer strategies for managing them effectively.
Overview of Depression and Its Physical Symptoms
Depression is a complex mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities. While these emotional symptoms are widely recognized, many people are unaware of the physical symptoms that often accompany depression. These physical signs can include chronic fatigue, sleep disturbances, digestive issues, and more, each contributing to the overall burden of living with depression.
The Connection Between Mental Health and Physical Symptoms
The relationship between mental health and physical symptoms is deeply intertwined. When the brain is affected by depression, it can lead to changes in the body’s functionality due to hormonal imbalances, heightened stress responses, and other physiological changes. Understanding this connection is crucial in identifying the physical symptoms of depression and finding ways to alleviate them.
Common Physical Signs of Depression
Recognizing the physical symptoms of depression is a critical step toward comprehensive treatment and management. Here are some of the most common signs:
Fatigue
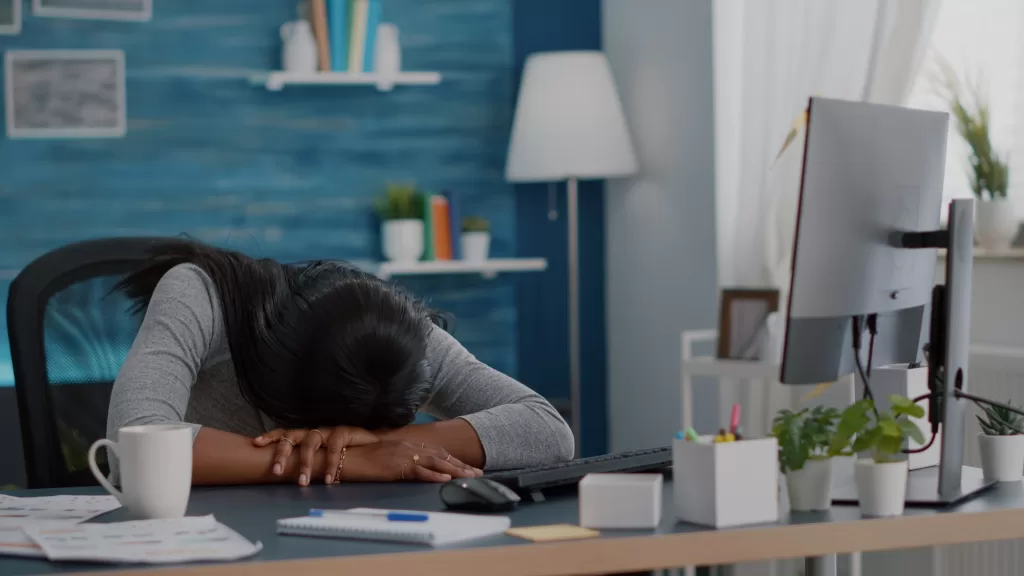

One of the most prevalent physical symptoms of depression is fatigue. Unlike regular tiredness, depression-related fatigue is persistent, making it challenging to perform daily tasks. This fatigue can stem from a combination of poor sleep quality, lethargy, and the overwhelming emotional weight of depression.
Changes in Appetite or Weight
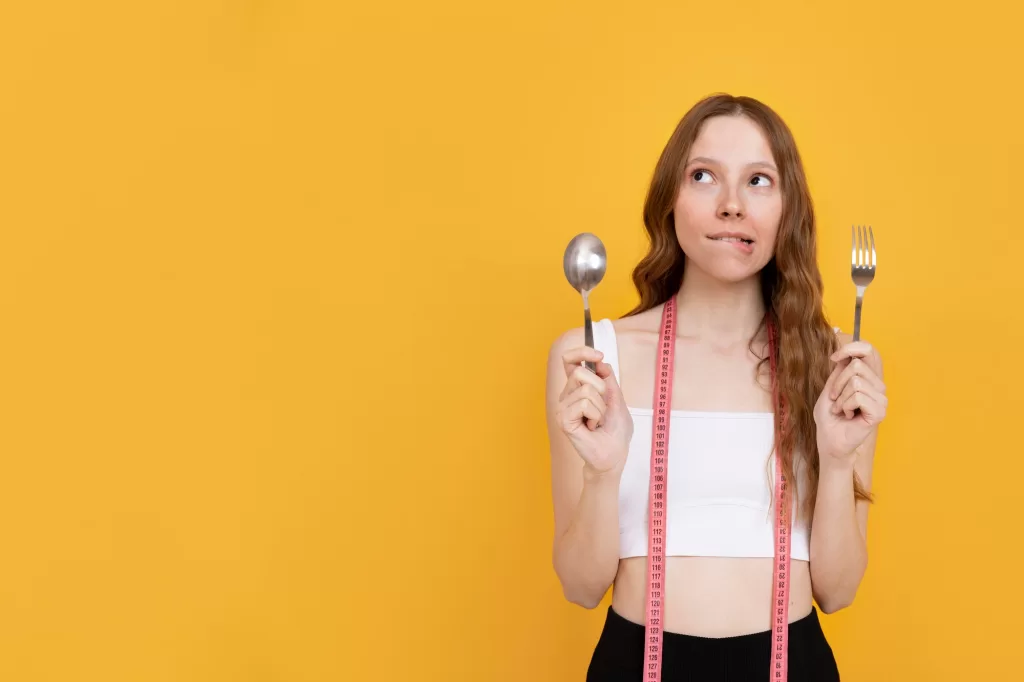

Depression can lead to significant changes in appetite, resulting in either weight gain or loss. Some individuals may experience a reduced appetite and lose weight without trying, while others may gain weight due to cravings for high-calorie comfort foods. These changes can have further physical health consequences and may affect self-esteem and body image.
Sleep Disturbances
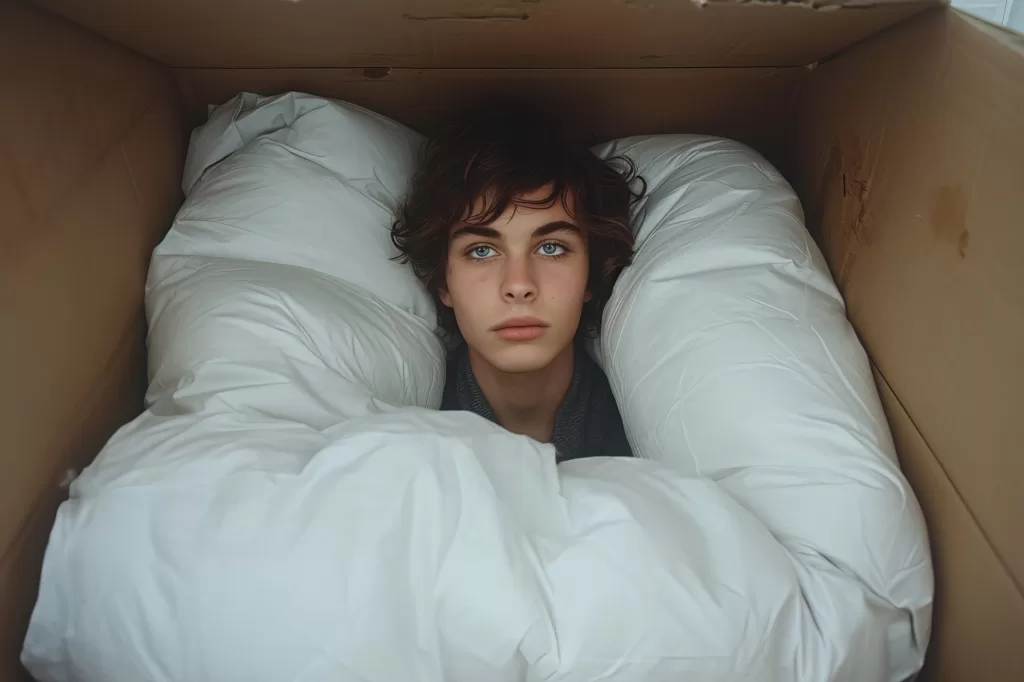

Sleep issues are common in those with depression, manifesting as insomnia, hypersomnia, or disrupted sleep patterns. Insomnia involves difficulty falling or staying asleep, while hypersomnia is characterized by excessive sleepiness and prolonged sleeping hours. Both conditions can exacerbate feelings of fatigue and impact mood and cognitive function.
Aches and Pains
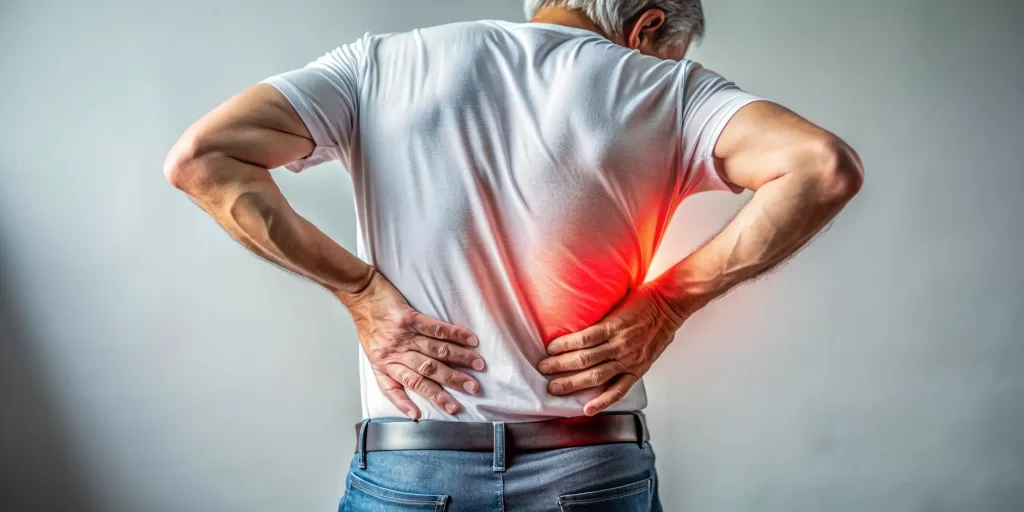
Depression can manifest as unexplained physical pain, including headaches, joint pain, back pain, and muscle aches. This pain can be chronic and resistant to traditional pain relief methods, contributing to a cycle of discomfort and emotional distress.
Digestive Issues
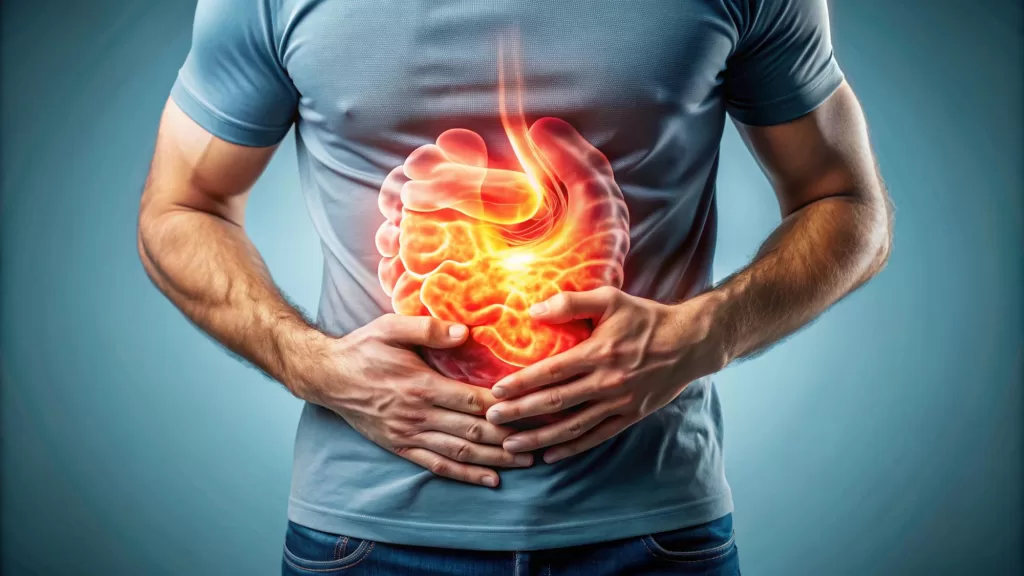
Gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, diarrhea, or constipation are often overlooked as symptoms of depression. The brain-gut connection is a growing field of research, highlighting how mental health directly influences digestive health. These issues can cause significant discomfort and may lead to further complications if not addressed.
Impact of Physical Symptoms on Daily Life and Well-Being
The physical symptoms of depression can severely affect one’s quality of life, making everyday tasks seem insurmountable. They can hinder productivity at work, strain personal relationships, and reduce overall life satisfaction. Furthermore, these symptoms often perpetuate the cycle of depression, as physical discomfort can lead to increased feelings of hopelessness and frustration.
Strategies for Managing and Improving Physical Symptoms of Depression
Addressing the physical symptoms of depression is an integral part of effective depression management. Here are several strategies to help alleviate these symptoms:
Regular Exercise
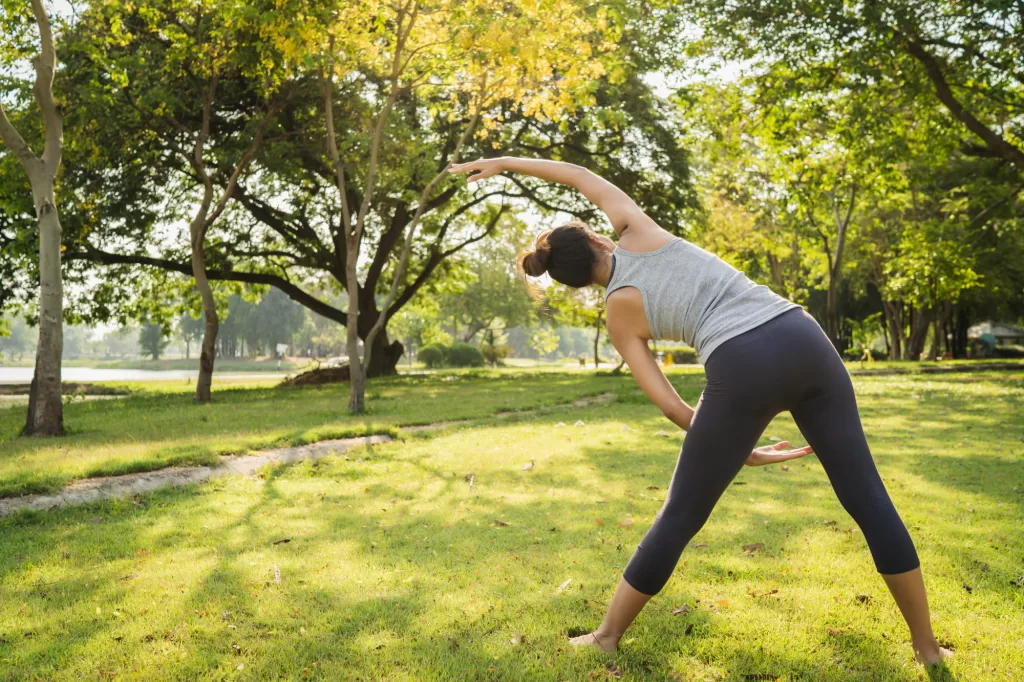

Physical activity is a powerful tool for combating depression. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters, and can help reduce fatigue, improve sleep, and alleviate pain. Even small amounts of daily exercise, such as walking or stretching, can produce significant benefits.
Healthy Eating
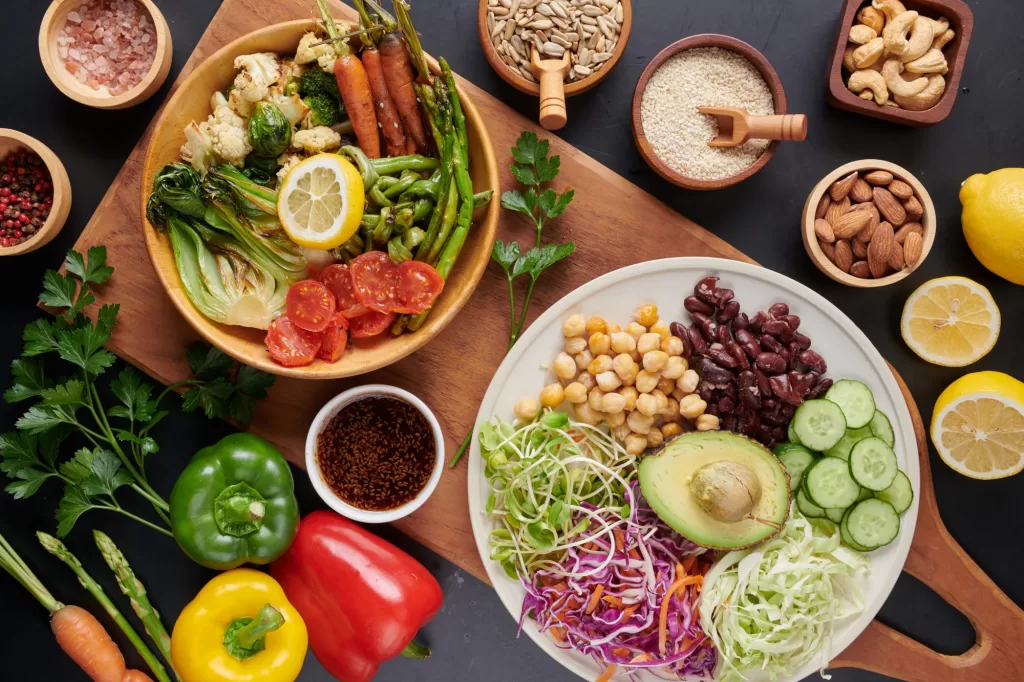

A balanced diet rich in nutrients can support mental and physical health. Foods high in Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins, such as fish, leafy greens, and fruits, can help reduce inflammation and regulate mood. Avoiding processed foods and excessive caffeine and sugar can also minimize mood swings and digestive issues.
Adequate Sleep
Establishing a consistent sleep routine is crucial for managing depression. Practice good sleep hygiene by setting regular sleep and wake times, creating a restful environment, and limiting screen time before bed. Sleep aids, such as relaxing teas or melatonin supplements, may also be helpful.
Seeking Professional Help
Professional intervention is often necessary to address both the mental and physical symptoms of depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication can provide relief from depressive symptoms. Additionally, a healthcare provider can offer guidance on managing physical health concerns related to depression.
Conclusion
Recognizing the physical symptoms of depression is an essential component of comprehensive care. By understanding the link between mental health and physical symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition. Strategies like regular exercise, healthy eating, adequate sleep, and professional guidance can offer significant relief.
If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, remember that help is available. Prioritizing both mental and physical health is key to living a fulfilling life. For more tips and support, visit our website at healthfunda.net. Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for personalized advice and assistance. Together, we can combat the challenges of depression and improve overall well-being.


